Estimated Reading Times: 6 minutes.
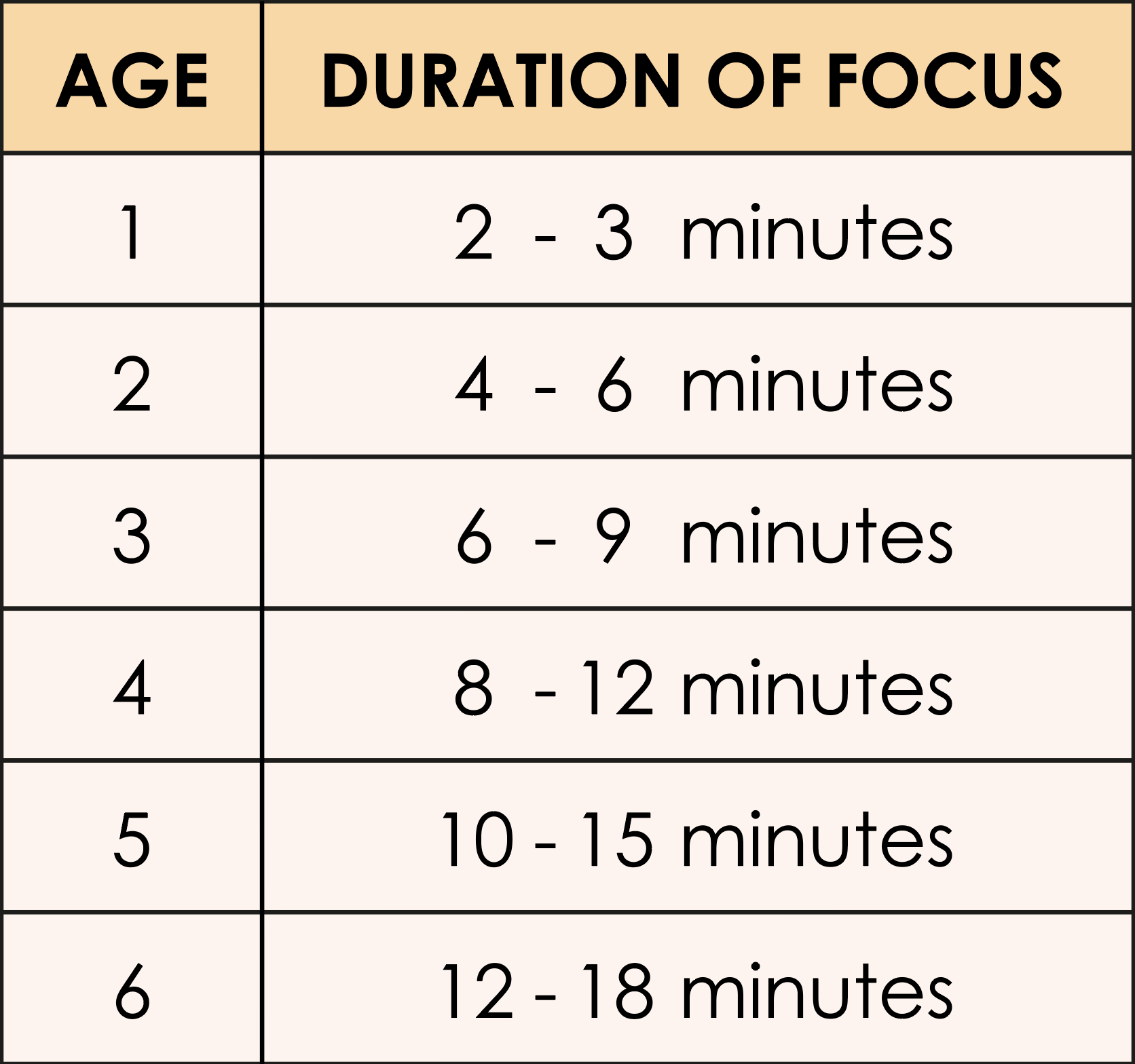
Have you ever told a child to focus but to no avail? This article will give you some insights on how long children’s attention span generally is, as well as ways to help them improve their ability to focus. First and foremost, a child’s maximum attention span is about two to three times his age; as such, a four-year-old child will be able to focus on an activity for about 12 minutes at most.
How to increase their attention span?
There are various ways that adults can adopt to help improve a child’s ability to focus for a longer period of time.
1. Give clear and concise instructions
When asking a child to complete a task, like wrapping a giftbox, an adult ought to make the instructions short and simple. If a child does not understand what he has to do or finds the task too difficult, he might just space out and disengage. What we can do is to break down the task into simple steps, for example “please put the gift into the box.” Once he is done with this step, we can then add on: “now, let’s place the box onto the wrapping paper” and so on.
If a child is able to execute a task step-by-step with bite-sized instructions, he will feel less overwhelmed and hence will be more able to focus better. You might also want to get the child to repeat your short instruction back to you to ensure that he is focused on what he is supposed to do.
2. Make sure the child is well-rested and nourished
A child is able to focus better if he has had ample rest and good nourishment. Preparing nutritious snacks for the child as well as letting the child take adequate rest are important in preserving his mental and physical strength. If an activity is too time-consuming, it is advisable to let the child take a short break in between or before moving on to the next activity. During this short break, the child may want to have a quick bite or move around to “recharge”.
3. Give praise
Positive reinforcement goes a long way in helping a child develop good attention span. A child might lose interest in completing a task if praise is scarce. However, the praise should not just be about the outcome, but also the process. Hence, even if a child did not achieve the desired outcome (e.g. to write his name) despite his best efforts, we can still tell him that we acknowledged his eagerness to try (e.g. “it is great that you are trying your best to write your name!”). This will motivate the child to want to concentrate more in the future, as he knows that his hard work is being recognised.
4. Establish routines
Children tend to perform better with a fixed routine. Therefore, allocating a fixed schedule for different activities will teach the child to know when is the right time to do something. This aids in developing their attention span as their brains will be attuned to doing a particular task at a specific time.
5. Appeal to the child’s interests
One way to ensure that you have the child’s attention is to take into account his personal interests when planning activities. It might be difficult to keep a toddler focused during activities that involve sitting and listening, unless the activities are engaging and motivating enough to hold their interests. Thus, if a child likes automobiles, you may want to prepare a game that involves cars and trucks to keep him engaged for a prolonged period of time.
6. Reduce screen time and other distractions
The constant absorption of on-screen images is detrimental to a child’s attention span as well as his language and cognitive development. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends avoiding screen time as much as possible until a child reaches two years of age. Reducing a child’s screen time will boost the development of his attention span. In lieu of watching videos, there are various activities that a child can undertake and some of these activities will be discussed in the last section below.
Apart from technological distraction, other distraction in the form of noise or nearby toys may be present. It is best to eliminate such distractions so that the child can fully focus on his tasks.
Activities to help enhance a child’s focus
You can help to increase a child’s attention span with these fun activities:
• Memory
Memory is a card game where picture cards are placed face down, and players take turns randomly selecting two cards and flipping them over. If the cards match, the player removes the pair from the array of cards and collects them. If the cards do not match, the player flips the cards back over, ending their turn. The goal is to collect the greatest number of matching pairs.
Memory teaches children to concentrate and pay close attention to the position of each card and the picture on each card that is flipped so they can find matching pairs. When playing the game with toddlers, it may be helpful to begin with only a few pairs of cards to prevent children from getting frustrated because they can’t find matching cards.
• Jigsaw puzzles
Jigsaw puzzles improve children’s attention by requiring them to focus on one task for a long time. Even simple jigsaw puzzles with only a few pieces require children to focus on arranging and orienting the pieces, which can increase the amount of time they spend on the task beyond their typical attention span.
• Bead jewellery
Creating bead jewellery requires that children thread a piece of yarn through the holes in the beads. This activity improves children's focus, concentration, and fine motor skills as they pay close attention to the beads and yarn and carefully thread the beads onto the yarn without missing the holes.
• Spot the difference
Spot-the-difference puzzles improve children’s concentration and encourage them to focus on details. These puzzles are almost identical illustrations that children can look at carefully to identify the parts of the illustrations that differ.
Is a child’s short attention span a cause for concern?
If the child:
• seems easily distracted and has difficulty paying attention to/concentrating on age-appropriate tasks;
• struggles to complete his tasks;
• cannot sit still and fidget a lot; and/or
• tends to interrupt others while they are talking, these might signal that he needs intervention from a specialist to tackle potential learning difficulties.
Back to blog main page | Go to Bilingual Class | Solo-Class | Main page